Defect Life Cycle In Software Testing - Phases & Outcome

Understanding the defect life cycle in software testing is important for successful software development. For any software development project, the primary concern is defect tracking. When the software feature does not perform as intended, then it's called a bug or defect. These issues can be created due to coding errors, design flaws, requirement misunderstandings, or even environmental issues.
To remove this, the development team is following the defect life cycle process. It's also called the bug life cycle.
In this blog, we will learn the actual process of the defect life cycle in software testing and all the other details around it.
Let's bounce.
What Is A Software Bug
Before all the serious talk, let's learn about bug definition in software testing.
A software bug is a faults, flaw, or error that create an unexpected outcome. Sometimes when we face these issues, we face several problems, including system crashes or freezes, or erroneous and insufficient output. In the long run, it can cause serious damage to the software
- Monetary losses
- Security flaws
- System failures
A study in the NIST report found that software bugs or buggy code cost the us economy around $59 billion. A buggy Therac-25 radiation therapy machine caused the death of a patient in the 1980s. So, before processing any software for deployment, the defect life cycle in software testing is important.
What Is the Defect Life Cycle in Software Testing
The defect life cycle, also known as the bug life cycle, is a process that begins after a defect is identified and continues until it's successfully resolved and verified.
If we describe it more simply, then it is the journey of a defect within the software development and testing process. This stage of the working process begins when a tester finds a software bug and then resolves it. After resolving the problem, they ensure it won't recur. The importance of the defect life cycle is many. Includes:
Importance of the Defect Life Cycle
- Provides a systematic way to handle defects.
- Prevents duplication of efforts.
- Improves communication between testers, developers, and managers.
- Helps in prioritizing defects based on severity and impact.
- Ensures that no defect is left unresolved or ignored.
Who Perform A Bug Life Cycle in Software Testing
It's not a one-man army game. In every stage, there are different people who perform different responsibilities. It's not like a tester does all the jobs and all the work is done.
|
Role Or Name |
Responsibility In The Defect Life Cycle |
|
Tester / QA Engineer |
They basically detect and report bugs with the defect tracking tools. They also provide details like steps, severity, screenshots, and logs. After fixing it, they also retest it and verify the results, reopen it if still present and then close the bugs. |
|
Test Lead / Project Manager |
Review reported bugs and assign a developer to those bugs, and sometimes priority and severity for business needs. |
|
The developer plays a big role here. They analyse it, confirm, validate and fix the defect of the code. If the bug is fixed, then change the bug status and communicate with the QA team for verifications. If invalid marks are rejected, it is a duplicate or a bug. |
|
|
Business Analyst (BA) |
Validates if the bug affects business logic or requirements, and may prioritize certain issues. Can also participate in UAT to verify critical fixes. |
|
Client / End User |
They give their reviews about the big fixes during the user acceptance testing (UAT) phase. If the work meets the expected results they want, then go for the final closure. |
All of those people are really working on a successful project and making sure the software meets the exact requirements and generates some revenue. This defect life cycle, or bug life cycle, has many different stages. Let's check all of those in the next sections.
What Are the Different Stages of Defect Life Cycle
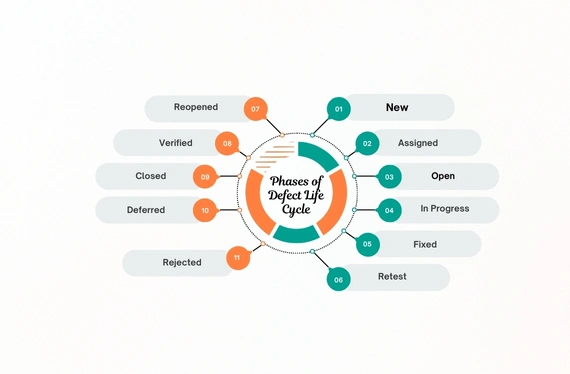
In any software development project, bugs make a huge impact on the expected outcome. Without proper software testing and proper checking, the software development project might be delayed. Not only delayed, but also increased the cost of the development. Most of all, it gives users a poor user experience that can lead to a bad reputation for the organisations.
At Bdtask (best software company in Bangladesh) every software project goes through a structured Bug Testing Life Cycle (BTLC) to ensure the highest quality standards. The QA team at Bdtask follows each phase — from bug identification to closure — using advanced testing tools and methodologies. Although, the bug testing life cycle is important and it's mandatory for every project. Still, you need to follow some stages. Check it one by one.
New
Responsibility: Tester / QA Engineer
The very first stage of the defect life cycle in software testing is the "new" stage. When a software development project first identifies any bugs or defects, it is referred to as new. So after detecting the bugs, a tester or QA engineer has some responsibilities. They log in to some renowned bug tracking tools like Jira, Bugzilla, or Mantis to track them. They do some paperwork. They find out all the details about the bugs, what the reason for it is, and what the variant is and much more.
Entry Criteria
- A tester has identified a defect
- Defect tracking tool with complete details
They go into the details below, such as:
- Defect ID (automatically generated by the system)
- Summary/title of the bug
- Description (steps to reproduce)
- Severity (impact on system functionality)
- Priority (urgency of fixing)
- Environment details (browser, OS, version)
- Supporting evidence (screenshots, logs, videos)
Proper documentation is important in this stage. It helps the developer to understand the issues easily and to solve the problem quite easily and accurately.
Assigned
Responsibility: Test Lead / Project Manager
After detecting the software bug, it's time to assign someone to fix it. So this responsibility goes to the test lead or the project manager. They check all the details of the bugs and discuss them with their available team member. Which group of developers are suitable for this problem? Below, you get an idea about it.
|
Bugs |
Assign developer |
|
UI/Frontend Bugs |
Frontend Developers |
|
Backend / Logic Bugs |
Backend Developers |
|
Database Bugs |
Database Developers / DBAs |
|
Integration Bugs |
Full-Stack Developers / Integration Specialists |
|
Security Bugs |
Security Developers / DevSecOps |
|
Performance Bugs |
Performance Engineers / Backend Developers |
|
Configuration / Environment Bugs |
DevOps / System Administrators |
|
Cross-Browser / Device Bugs |
Frontend QA & Frontend Developers |
|
Third-Party Dependency Bugs |
Integration Developers |
Responsibilities in this stage
- Validate whether the bug is a genuine issue or a misunderstanding.
- Decide its priority (business-driven urgency)
- Allocate the defect to a developer who owns that part of the application
This stage is really important because it speeds up the workflow, and the right developer does their job best.
Open
Responsibility: Developer
After assigning the developer for the work, it's time to hand over all the data or resources to the developers. This stage we call the open stage. In this stage, developers have access to all the real data of the bugs. After getting all the files they need, they don't immediately jump into working. If they need any information about the project, bugs or anything else, then they will have a meeting with the project manager or QA team. After that they they go through a systematic process to understand and validate the issues.
Responsibility in this open stage :
- Reproduce the Bug
- Run the application in the same environment (browser, OS, device, test data) where the tester found the issue.
- Track logs & Code
- Track error logs, stack traces, or debug outputs.
- Find out affected code modules, functions, or database queries.
- Validate the Bug issues
- Decide if the reported issue is truly a defect or not.
- Perform root cause analysis (RCA)
- Estimate the time to complete the task
- Talk with the project manager if it requires major changes.
- Collaborate if Needed
- If the bug spans multiple modules (e.g., frontend + backend), discuss with other developers or integration engineers.
- Prepare Fix Strategy
But there is still a question in the defect life cycle. If the information is not valid, then what should the developer do? The answer is quite simple. If the information is not valid, then it will mark it as rejected, duplicate, not a bug or deferred.
In Progress
Responsibility: Developer
So, after confirming the bug or defect is valid, the developers are working on it. This stage is called the resource-heavy stage. But why? This stage involves coding, testing, and ensuring the fix doesn't break any other part of the code.
The key importance of this stage
- Modify the code or configuration to resolve the issue
- Write unit tests to validate the fix
- Collaborate with others if the defect spans multiple modules
Fixed
Responsibility: Developer
This is the last stage where developers work on the pitch. They work on the time limit of the project, and if the problem is fixed, then it's marked as a Fixed stage. If they don't solve the problem, then they talk with the project manager to extend the duration of the project. So most of the time they complete the work before the deadline.
Key things to do in this stage :
- Code changes are committed to the repository
- Unit and integration tests are executed
- The updated build is shared with the testing team
So here the developer's work is done, and they submit it to the tester team, who retest it again.
Retest
Responsibility: Tester / QA Engineer
So, after the end of the fixed stage in the defect life cycle in software testing, it's time to check it again. The tester and the QA engineer check it again. They did the testing process the same as the previous time. If it passes, then it's going to the verified stage; if it doesn't, then it's sent to the reopened stage.
Key responsibilities in this stage :
- Retest the exact scenario described in the bug report
- Perform regression testing to ensure that the fix hasn't introduced new issues
- Validate the environment in which the defect was reported
Always make sure everything is well-documented and well-organised.
Reopened
Responsibility: Tester / QA Engineer
The tester and the QA engineer perform this stage. This stage is reopened if the tester team and the QA engineer find the old defect again. They then sent it to the developer section and told them to fix it again.
Key work at a glance
- Provide additional evidence if needed
- Clearly explain why the fix failed
Prevents "false closure" of unresolved bugs. This cycle between Fixed → Retest → Reopened can repeat until the defect is resolved correctly.
Verified
Responsibility: Tester / QA Engineer
This stage defines that the software development project has already fixed the bug, and the tester again tests it and marks it verified. Verified means the software defects are successfully solved and ready to proceed in the next sections. It's also open for others to test for any issues to find.
Responsibilities
- Conduct final confirmation tests
- Check that the bug does not recur in similar scenarios
If the stage is complete, then it's officially verified for closure sections.
Closed
Responsibility: Tester / QA Engineer (sometimes Client/BA)
It is the final stage of the defect life cycle in software testing. In this stage, the defect status is permanently closed. This stage defines that it is no longer active in the system and is considered resolved permanently. So in this stage, everything is well documented for further usability. Check the duration time and also check if it fulfils the criteria assigned by the team manager or product manager. Sometimes, clients check the documentation of the whole project. So make sure the documentation is well prepared and accurate.
Key note of the closed stage:
- Was reproducible earlier, but is no longer present
- Meets the acceptance criteria defined in the bug report
- Has not caused any side effects in related modules
Before closing this stage, remember the following:
- Defect is no longer reproducible
- Acceptance criteria are met
- Regression testing is successful
- Environment validation is done
- No duplicate reports exist
- Approval from stakeholders (if required)
- Proper documentation is updated
- Tester must update test results, attach evidence (screenshots, logs, test cases), and add closure notes.
- Defect status history is clear
- Linked issues are resolved
This is where the official bug life cycle is closed and ready for the other stage of software development. It serves as a confirmation that the bug will not impact the software product anymore, providing confidence that the application is stable and ready for release. But still, there are two options to remember, which are deferred and rejected.
Exit Criteria
- The developer has successfully fixed the defect.
- The tester has retested and verified the fix
- The defect is closed in the tracking system
Deferred
If the defect or bugs are not the top priority, then it goes in this stage. Sometimes the developer or the team declare that these bugs can be solved in the next update. But remember, high-risk bugs are not referred to in this stage.
Rejected
This stage is basically open to a false alarm. It occurs when a stage risk is conducted by a developer or lead and determined to be invalid or unnecessary for fixing.
A bug can be rejected for different reasons. Include:
- Duplicate purpose of the same data already issued earlier.
- incorrect setup, test data, or configuration rather than application logic
- Out of scope
Follow all those stages to help find out the bugs in software or app development and resolve them. Still need to maintain a proper plan and estimate everything. Models like the agile model or the V model use this DLC to make positive outcomes and help to deploy a bug-free software experience.
Final Thought
The defect life cycle in software testing is obviously a key to delivering high-quality software and customer satisfaction. It also helps to reduce the manual overhead, speed up resolution, and maintain complete transparency across all roles involved.
A well-managed defect life cycle not only improves collaboration but also saves time, money, and effort in the long run for a software company.
FAQs
What Are the Different Types of Software Bugs?
Here are the most common types of bugs found by the testing in different projects, including:
- Functional Bugs
- Logical bugs
- Workflow
- Unit level
- System-level integration bugs
- Outbound bugs
- Security bugs
- Performance bugs
- Usability bugs & more
What Is the Difference Between Defect Status Vs. Defect State?
Defect Status is the current condition of a defect at a given point in time . On the other hand, the defect state is the overall stage of progression.
What Are the Benefits of Using Software Defect Tracking?
There are many benefits of using the defect management life cycle in any software development project. include:
- High-quality software
- Saves time and cost
- Improves collaboration
- Lower cyber attack possibility
- Transparency in defect handling for stakeholders
- customer satisfaction
What Are the Tools for Managing the Defect Management Life Cycle?
There are different types of tools available online and worldwide . But the renowned software is:
- JIRA (used in Agile projects)
- Bugzilla (Open-source, flexible, and widely adopted for bug tracking)
- Mantis Bug (Tracker open-source tool with user-friendly features)
- Redmine (Web-based project management and defect tracking tool)
Why Is the Defect Life Cycle Important in Software Testing?
It ensures that defects are handled systematically, avoiding duplication and improving software quality.
What Is the Difference Between the Defect Life Cycle and the Bug Life Cycle?
They are the same; “defect” is the professional QA term, while “bug” is informal.
Who Is Responsible for the Defect Life Cycle?
Testers, developers, QA leads, and project managers are all involved in the defect life cycle of software testing.
How Do You Track Defect Status in Real Projects?
By using defect tracking tools like JIRA, which record status changes and assignments.
Can a Defect Be Reopened After Closure?
Yes, if the defect reappears during further testing, it is reopened and reassigned.
What Is a Deferred Defect in Testing?
A defect postponed for fixing in future releases due to low priority or dependencies. It's for the low-priority defect that can not affect the system so much.
How to Improve Defect Life Cycle Efficiency?
By writing detailed defect reports, prioritizing issues correctly, and conducting regular defect triage meetings.










