What Is MVP In Software Development - Process & Types

Software development is costly for sure. If you have the option to check the exact performance before deploying the full software, then how was that? The answer is definitely yes. MVP in software development plays this role. But what is mvp in software development?
An MVP is a process that helps businesses test their software ideas with real users before investing significant time, resources, and money.
Instead of building a full-fledged product with dozens of features, companies focus on creating a basic but functional version. Deploy it to early users, and if their feedback is positive, proceed with full functional work.
It's definitely a good process in the software development life cycle. It helps to determine whether the desire to develop software leads to the expected outcome.
In this blog, we learn and find out everything about what is MVP in software development, its benefits, the working process and why it's important.
Let's start learning then.
What Is MVP in Software Development
MVP = Minimum Viable Product
This process is getting popular through the Lean Startup methodology. It was introduced by the famous Eric Ries.
An MVP in software development plays a huge role in running a successful software development project. It's basically an early stage of building a proper, full-featured software. It's a process of building the simplest version of a product that includes only the core features required to solve a specific problem for early users and to gather feedback. If the feedback is quite good and beneficial, then the product's development is good to go.
The main goal of this process is learning, not perfection. It allows teams to test assumptions, understand user behaviour, and make data-driven decisions for future development.
The responsibility of MVP in software development:-
- Building products faster
- Learning from real users
- Reducing waste in development
- Improve products based on real feedback.
- Avoid building features users don’t need & more.
What Is the Primary Purpose of an MVP in Software Development
In the world, people have a specific purpose. There is no alternative in this section either. MVP or (Minimum Viable Product) also serves a purpose. The main purpose of the MVP in software development is validation. Software companies use this process to determine whether a target project is profitable. The primary purpose of this software development process is given below:-
- Validate a business idea.
- Test market demand
- Identify target users
- Reduce financial risk
- Speed up time-to-market
- Collect user feedback early.
- Improve product-market fit
Key Characteristics of an MVP in Software Development
Instead of investing heavily in a fully developed product from the start, an MVP allows businesses to validate ideas, reduce risk, and accelerate time-to-market. Below are the key characteristics that define an effective MVP in software development. Many companies offer this service so that they can check the output and then work in detail. Bdtask also offer custom software development services at all stages with their professional developer with reasonable price range.

Core Functionality
The most important characteristic of an MVP is its focus on core features only. An MVP does not attempt to solve every problem or satisfy every user's needs. Instead, it addresses the primary pain point that the product is designed to solve.
Any feature that does not directly contribute to this core value is intentionally excluded. This approach ensures faster development and clearer validation of the product idea.
User-Centric Design
An MVP is built with real users in mind. Even though it is a simplified version of the final product, usability should never be compromised. The interface and user experience must be intuitive enough for users to understand and interact with the product easily. Early user feedback plays a crucial role in shaping future improvements and feature additions.
Fast Time to Market
Speed is a defining trait of an MVP. The goal is to launch the product as quickly as possible to test assumptions and capture early market response. By shortening development cycles, businesses can stay competitive, identify flaws early, and adapt faster based on user behavior and feedback.
Cost Efficiency
An MVP is designed to minimise development costs. By limiting features and focusing on essentials, companies avoid unnecessary spending on complex functionalities that may not be needed. This is especially valuable for startups and small businesses with limited budgets, as it allows them to validate ideas without heavy financial risk.
Scalability Potential
This means the underlying technology and design should allow for future expansion without requiring a complete rebuild. A well-planned MVP can evolve smoothly into a full-featured product as user demand grows.
Feedback-Driven Development
An MVP thrives on continuous feedback. User interactions, analytics, and direct responses help teams understand what works and what doesn’t. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making, ensuring future development aligns with actual user needs rather than assumptions.
Measurable Success Metrics
A successful MVP includes clearly defined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as user engagement, retention rates, or conversion metrics. These measurements help evaluate whether the product is achieving its intended goals and whether it is ready for further investment and development.
Iterative Improvement
An MVP is not a one-time release; it is the starting point of an iterative development process. Based on insights gathered from users, the product is refined, optimized, and expanded over time. Each iteration adds value while maintaining alignment with business objectives.
Top Differences in MVP vs Prototype vs PoC
To learn more about MVP, you need to learn the difference between MVP vs Prototype vs PoC. It helps build a solid Software development life cycle model. But what is MVP vs Prototype vs PoC? Are those really similar or not? Let's find out through this comparison table.
|
Factor |
MVP |
Prototype |
PoC |
|
Definition |
A real product used by real customers |
How the products work and look |
Proves that the idea is technically possible |
|
Lifecycle stage |
Early product stage |
Pre development stage |
Idea stage |
|
Target audience |
Real market users |
Designers & test users |
Internal stakeholders |
|
Functionality |
Core working features |
Partial |
Very limited |
|
Development time |
Real users |
Weeks |
Days to weeks |
|
Cost |
Higher |
Medium |
Low |
|
UI/UX |
Important but minimal |
Very important |
Not required |
|
Used for |
Product launch |
User flow testing |
Tech experience |
|
When to used |
To find the output of the project |
Test UI/UX, early design feedback, investors show ideas, and user flow |
Using new technology, if any complex algorithm is involved, test integration, and convince stakeholders |
|
End goal |
Product market fit |
Usability validation |
Technical validations |
Here is the total difference among them. But if we make it short format, then it will be:-
- Test the new technology:- PoC
- Validate Ui/UX design:- prototype
- Test business ideas in the market:- MVP
- Visually checking the ideas:- Prototype
- Start generating users or revenue:- MVP
Types of MVP in Software Development
In software development, MVP is not just a single fixed format. It depends on the different criteria and requirements. Each is designed to validate an idea in a specific way. Choosing the right MVP model is based on the goal, budget, timeline, and target audience. Normally, it's basically in two types
- Low-Fidelity MVPs
- High Fidelity MVPs
Low-Fidelity MVPs
Low-Fidelity MVPs are basically focused on validating an idea with minimal development effort. Its duration is 2-6 days, and it uses tools like landing pages, sketches, or videos to gather early user feedback. Low-Fidelity MVPs come in various types as well.
- Landing Page MVP
- Explainer Video MVP
- Wireframe or Mockup MVP
Difference in Low-Fidelity MVPs
|
Difference |
Landing Page MVP |
Explainer Video MVP |
Wireframe or Mockup MVP |
|
Definition |
A single webpage is created to explain the product idea, features, and benefits |
A short video is created to show how the product would work |
Test the design and user flow without writing code. |
|
Best for |
|
|
|
High Fidelity MVPs
It's basically advanced, functional prototypes before the main products are live. On the other hand, it is closer to real products. They involve actual development and provide working functionality to users. It also has types, and let's check it:-
- Single-Feature MVP
- Concierge MVP
- Wizard of Oz MVP
- Piecemeal MVP
Difference in high-fidelity MVP types
|
Factor |
Single-Feature MVP |
Concierge MVP |
Wizard of Oz MVP |
Piecemeal MVP |
|
Definition |
Building only one core feature instead of a complete system |
Services are delivered manually instead of through automation |
Fully automated system for users, but the backend operations are handled manually |
Combines existing tools and third-party services instead of building everything from scratch |
|
Best For |
|
|
|
|
Low-fidelity MVPs are ideal for early-stage idea validation. On the other hand, high-fidelity MVPs are better for real market testing and revenue generation.
Process of building MVP in Software Development
After covering the basics and the differences, let's move on to the most important part of the software development life cycle. MVPs in software development help save time, months, and, most importantly, money. Businesses create a smaller, focused version to test ideas quickly and cost-effectively. However, building an MVP requires a structured and strategic process. Following the right steps ensures that the MVP delivers real value and useful insights.
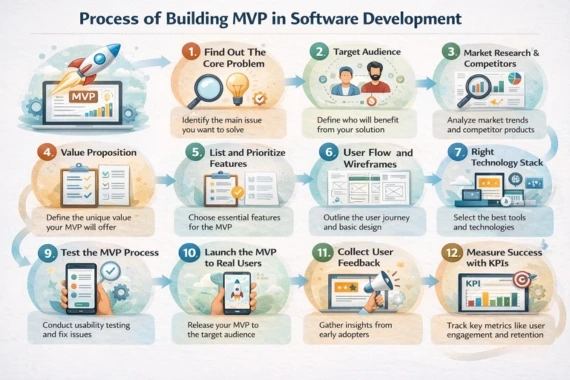
Find Out The Core Problem
Before starting any project or anything, a few things need to be settled down. So in that case, find out the problem or issues on that particular side. If the thing is a news management system, then find out which features users are not getting in the market. There is a proverb that every successful project starts with user problems. You can ask questions like
- What problem are users facing?
- Who is experiencing this problem?
- How are they solving it currently?
- Why is the existing solution not good enough?
The main goal of this stage is to define the pain point as clearly as possible. Otherwise, an MVP without a well-defined problem will lack direction and purpose.
Target Audience
So the first work is kinda done. The next very important step is to target the audience. An MVP should not focus on everyone. It's not good practice after all. Focusing on the specific audience makes the project more focused. So, create user personas that include:-
- Age, location, profession
- Behavior patterns
- Needs and expectations
- Technical ability
Collect the data on who the early users are and what motivates them. These are all the necessary steps to fill and go to the next steps.
Market Research & Competitors
Market research is primarily used to identify target users, their problems, market needs, competitors' limitations & more. To find out, focus on the market leaders and the features they offer. If you dont do market research in the early stage, it might be a lost project after building the MVP. Market research helps you to find out:-
- Analyzing competitors
- Understanding similar products
- Identifying market gaps
- Finding opportunities for differentiation
This market research aims to find the limitations of leading software and what you need to build to beat them.
Value Proposition
In this stage, you need to clarify why the customer or consumer should buy your MVP software. You need to focus on the following questions:-
- Why should users care about your product?
- What benefit will they get?
- How is your solution better than others?
Apart from that, you need to define also:-
- Core benefits of the products
- Unique features
- The main reason to choose your products.
An example will make it clearer. Suppose you want to deploy a restaurant software. In the market, there are many available options. But why do people choose your one and why do they implement it in your store? You need to focus on that.
List and Prioritize Features
The next one of what is mvp in software development is listing the features and prioritising them. So select all the features in the software for your desired project, then select some of them, but not all of them. Make a list like below :
- Must-have features
- Nice-to-have features
- Future features
But this time, you need to include only must-have features in your MVP. After this work goes well, go ahead with all the detailed features. This step prevents feature overload and keeps the product simple and focused.
User Flow and Wireframes
Before developing or starting any software testing process, it's important to know how users will interact with the product. So in that case, you need to visualise the whole process. You can get help from the graphics team to implement it. This stage includes:
- Designing user flow diagrams
- Creating wireframes or mockups
- Planning screens and navigation
Tools like Figma, Adobe XD, or Sketch can be used to create basic designs. This helps developers and stakeholders clearly understand the MVP's structure before coding begins.
Right Technology Stack
After all that, it's time to choose the right technology. The right technology or code can run the project smoothly like butter. You need to focus on the following things at first:-
- Speed of development
- Select the code
- Scalability
- Budget
- Team expertise
- Platform (web, mobile, or both)
- Right SDLC model
The goal is to choose technologies that allow fast development without compromising future growth.
MVP Using Agile Development
Now comes the development sections. So in that case, MVP and agile model are good to go. If you dont know about the agile development process, it is a model that helps process A-Z in software development. Following an exact software development model can help achieve the right outcomes.
Benefits of using Agile:-
- Short development cycles
- Continuous software testing
- Regular improvements
Instead of building everything at once, the team develops the product in small iterations called sprints.
Test the MVP Process
The process is short and does not take much time, unlike other software development processes; still, it needs to be tested throughout. Importance in software testing and the output is low bugs and a smooth user experience. This test includes:-
- Functional testing
- Usability testing
- Performance testing
- Security checks
The goal is to ensure that the core features work smoothly and provide a good user experience.
Launch the MVP to Real Users
If all the work, like development and testing, is done perfectly, it's time to deploy it to real users. But not whole in the market. The launch might be:-
- A beta release
- Limited user group
- Specific geographic market
- Early adopters
The purpose is not a perfect launch but a learning launch. Real users should start using the product as soon as possible.
Collect User Feedback
The heart of any software development process is user feedback. That can help make any project even better. But the question is: how can we make that happen? The process is simple . We can follow the following things:-
- User interviews
- Surveys
- Analytics tools
- In-app feedback
- Behavior tracking
The surveys help us understand how users actually interact with the software and the bugs they encounter.
Measure Success with KPIs
Another important aspect of an MVP software development plan is tracking the entire user feedback process. It helps to learn the exact KPI of the project. Track down like:-
- User sign-ups
- Active users
- Engagement rate
- Retention rate
- Conversion rate
- Customer feedback scores
These KPIs help determine whether the MVP is successful or needs major changes.
Iterate and Improve
Getting all the data from the shortlisted users, it's time to work on those reviews and suggestions. It helps to make this project more solid and user-friendly. It might be:-
- Adding new features
- Removing unnecessary ones
- Improving UI/UX
- Fixing bugs
- Enhancing performance
After all the improvements, it starts the final testing of the draft project and shares the outcomes and KPIs with the project holder. If they're ok with the result and it's time to finish, move on to the final stage.
Work on Full Product Roadmap
The final stage of the whole MVP software development is the work on the full product development roadmap. Once the MVP proves successful and achieves product-market fit, you can move toward building the full product. Create a roadmap that includes:
- Advanced features
- Scalability plans
- Long-term goals
- Monetization strategies
This is all about software development in MVP. Now you know what is MVP in software development is and how it actually works.
Final Note
The article provides an overall idea of what is MVP in software development and the overall process. In fact, building an MVP is not just about developing a small product; it is a strategic process of learning and validation. With this process, you can save valuable time and money and build better products. A perfect software development process for those who are really in doubt about investing in their project; they can easily do so with this process without spending all the money.
A well-planned MVP allows companies to move from idea to market quickly and confidently. Instead of guessing what users want, you let real data guide your product decisions.
FAQs
Is an MVP a Final Product?
No. An MVP is not a final product. It is an early version of the product designed only for learning, testing, and improvement.
What Is the Difference Between MVP and Prototype?
A prototype is a visual or clickable model used to test design and user flow, while an MVP is a real working product used by actual users in the market.
How Long Does It Take to Build an MVP?
Typically, an MVP takes around 1 to 4 months to build, depending on complexity, features, and development resources.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop an MVP?
MVP development cost varies based on scope and platform.
- Simple MVP: $5,000 – $15,000
- Medium MVP: $15,000 – $50,000
- Complex MVP: $50,000+
Note:- Its eally on the region and the local developer demands.
Who Should Build an MVP?
MVPs are useful for:
- Startups
- SaaS companies
- Entrepreneurs
- Enterprises
- Product teams
- Mobile and web app developers
Can an MVP Generate Revenue?
Yes. Many MVPs generate early revenue by solving a real problem with minimal but useful functionality.
What Features Should Be Included in an MVP?
An MVP should include only:
- Core problem-solving features
- Basic UI/UX
- Essential security
- Minimum functionality needed for real users
What Are the Benefits of Building an MVP?
Minimum Viable Product brings many benefits. Apart from that top key benefits to look at:-
- Faster time-to-market
- Lower development cost
- Reduced risk
- Real user feedback
- Better product-market fit
Is MVP Only for Startups?
No. Enterprises and established companies also use MVPs to test new ideas and innovations safely.
Which Methodology Is Best for MVP Development?
Agile methodology is best for MVP because it supports:
- Fast iterations
- Continuous improvement
- Flexible changes
How Do I Choose the Right MVP Type?
It really depends on the project. But in general, you need to focus on the following things:-
- Budget
- Timeline
- Complexity
- Business goals
- Target users










